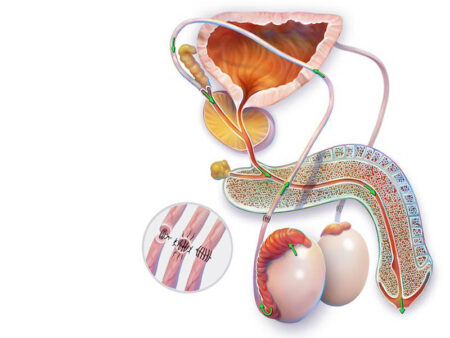
Vasovasostomy
Vasovasostomy
What is Vasovasostomy?
Vasovasostomy is a microsurgical procedure that reconnects the vas deferens, which were previously blocked during a vasectomy.
During a vasectomy, the vas deferens—the tubes that carry sperm from the testes to the ejaculatory ducts—are cut. In a vasovasostomy, the two severed ends of the vas deferens are rejoined under a microscope.
Reasons for Vasovasostomy
- Restoring Fertility: The main purpose of this surgery is to restore a man’s fertility after a vasectomy.
- Relief from Post-Vasectomy Pain: In some cases, vasovasostomy is performed to relieve chronic pain that may occur after vasectomy.
Success Rate
When performed with microsurgical techniques, vasovasostomy restores the presence of sperm in the semen in about 85% of cases, and leads to successful pregnancies in approximately 53% of cases.
The procedure is usually done in an outpatient surgery center or hospital under general anesthesia. It does not require hospitalization, and patients are discharged the same day.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
- A relatively safe and effective surgical option.
- Offers the possibility of achieving a natural pregnancy.
Disadvantages
- As with any surgery, there are risks such as infection and bleeding.
- The surgery is not always successful; in some cases, the reconnection may not allow sperm to pass through effectively.
Surgical Technique
- The patient lies on their back on the operating table.
- After general anesthesia is administered, the surgeon makes a small incision in the scrotum. Using a high-powered surgical microscope, the two ends of the vas deferens are identified.
- Fluid from the vas deferens is examined for the presence of sperm.
- If sperm are present, the surgeon reconnects the two ends using extremely fine sutures.
- The procedure typically takes 2–4 hours.
- It may take several months to over a year for sperm to reappear in the semen and for pregnancy to occur.
Follow-up Testing:
- A semen analysis is usually performed 2–3 months after surgery.
- A second semen analysis is done at 6 months post-surgery.
- If sperm are not detected or sperm counts remain low, additional semen analyses are repeated every 2–3 months.
Preoperative Instructions
- Shower and shave the genital and abdominal area.
- Stop taking blood-thinning medications such as Aspirin, Warfarin, or Heparin.
- Fast for at least 8 hours before surgery.
- Remove all jewelry, watches, and personal items before entering the operating room.
- Do not wear glasses, dentures, hearing aids, contact lenses, or prosthetics during surgery.
- Empty your bladder immediately before the procedure.
- Inform your doctor and nurse if you smoke or use other substances. Stop smoking at least 24 hours before surgery.
Postoperative Care
- First 24 hours: Complete bed rest.
- Wear tight underwear (supportive briefs or a scrotal support) for 6 weeks, including during sleep (except while showering).
- Shower 48 hours after surgery.
- Continue using supportive underwear during sports activities until pregnancy occurs.
- Return to light office work after 3 days.
- Avoid heavy physical activity and exercise for 4 weeks.
- Avoid sexual intercourse for 4 weeks.
- Have a semen analysis 1 month after surgery.
- Contact your doctor if you experience severe scrotal swelling, fever, chills, or significant pain.
- Schedule a follow-up visit 1 week after surgery.